Introduction

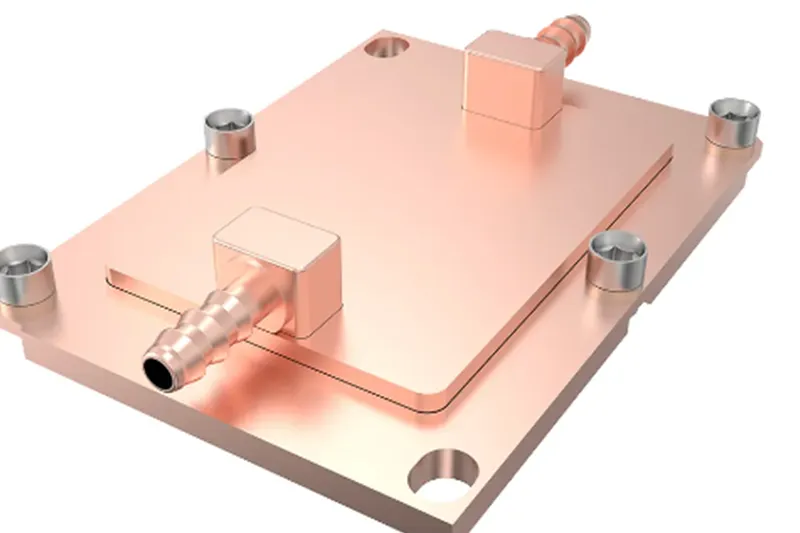
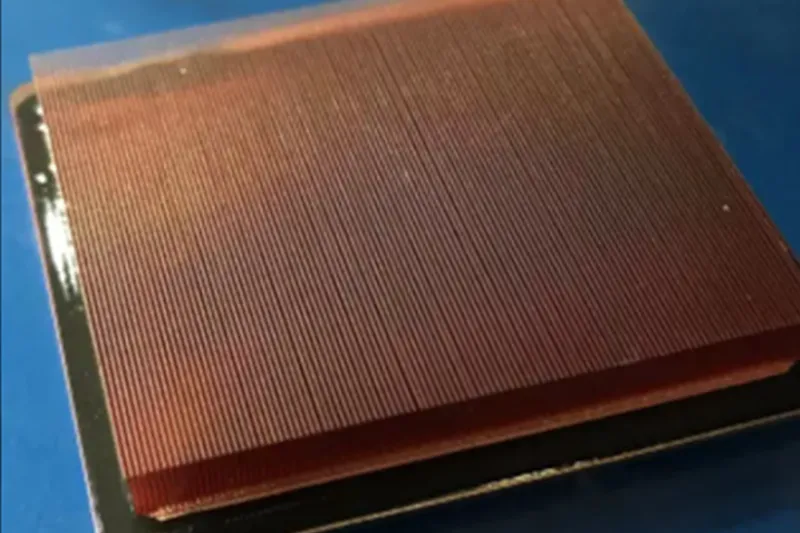
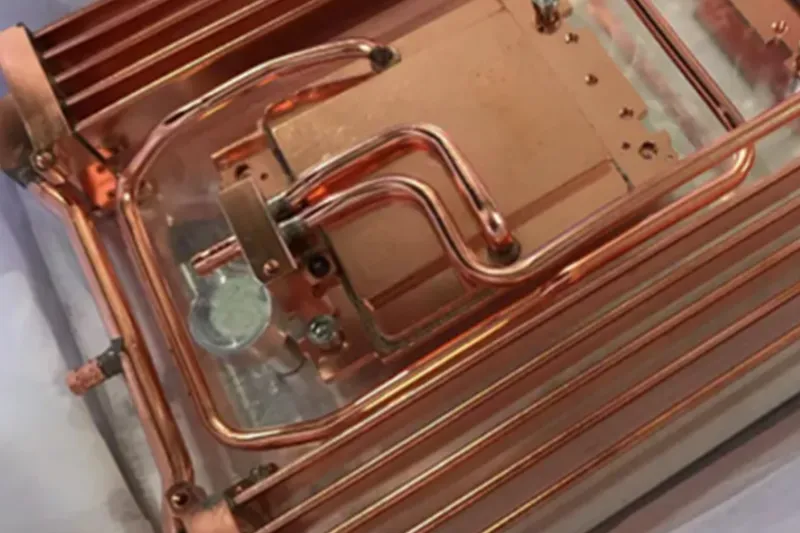
The brazing liquid cold plate is a pivotal technology in advanced cooling solutions. These plates offer unmatched efficiency and reliability, which is especially significant for manufacturers looking to customize cooling systems. This article aims to demystify the concept of brazing liquid cold plates, discussing their significance, construction, and customization for diverse applications.
The Significance of Brazing in Cooling Systems
Brazing technology plays a crucial role in the fabrication of liquid cold plates. It allows for the creating of complex internal structures that facilitate efficient thermal management. This is particularly important for applications requiring high-performance cooling in compact spaces.
Target Audience
This guide is designed for engineers, cooling system designers, and manufacturers considering custom brazing liquid cold plate solutions for their projects. Whether you want to enhance the cooling efficiency of electronic components, medical devices, or renewable energy systems, this article will provide you with essential insights into the design and application of these advanced cooling solutions.
Understanding Brazing Liquid Cold Plates
To fully appreciate the value of brazing liquid cold plates, it’s essential to understand what they are and how they function in cooling systems.
Definition and Basics
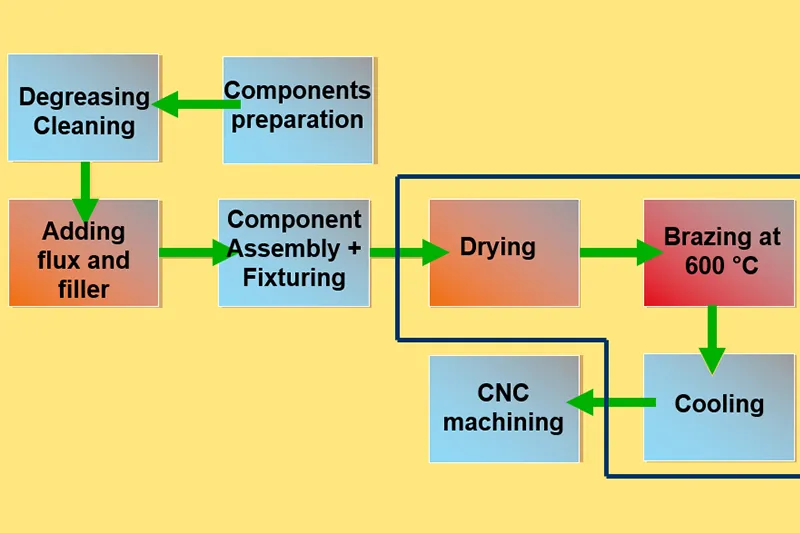
A brazing liquid cold plate is a heat exchanger that uses a liquid coolant to transfer heat away from hot components. It typically consists of metal plates with internal channels or passages where the coolant circulates. Brazing involves joining two metals by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint, which is crucial in creating these intricate internal structures.
Advantages of Brazing Liquid Cold Plates

- Efficient Heat Transfer: The brazed channels within the plate ensure optimal heat transfer, making these plates highly efficient for cooling applications.
- Customizable Designs: Due to the versatility of the brazing process, liquid cold dishes can be custom-designed to fit specific cooling requirements, accommodating various shapes and sizes.
- Durability and Reliability: The strong bond formed by brazing contributes to these cooling plates’ durability and long-term reliability, making them suitable for demanding applications.
The Brazing Process in Liquid Cold Plates
Understanding the brazing process is critical to appreciating the technical sophistication behind liquid cold plates. This section explores how brazing is applied in manufacturing these vital components.
Introduction to Brazing Technology
Brazing is a metal-joining process that involves heating a filler metal to a temperature above its melting point but below the melting point of the joined metals. This filler metal flows into the joint by capillary action and solidifies upon cooling, forming a robust and leak-proof bond. In liquid cold plates, brazing is used to seal the internal channels that contain the cooling fluid.
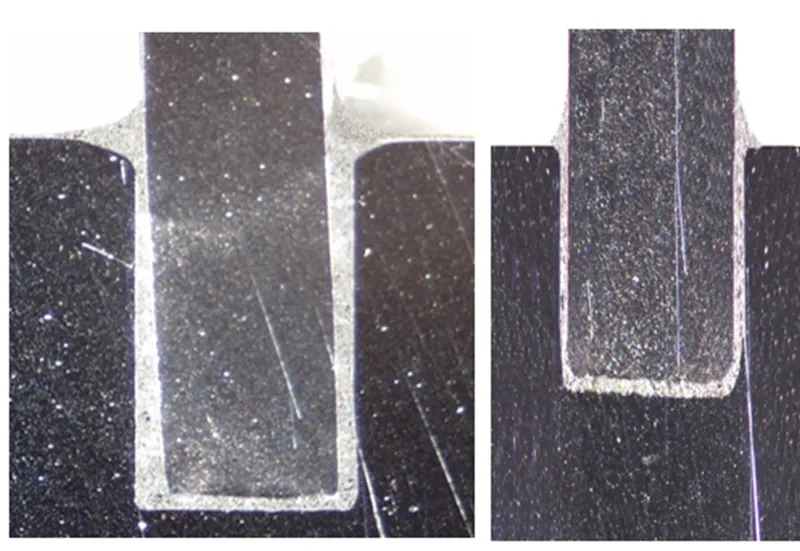
Material Considerations for Brazing
- Choice of Metals: The most common metals in brazing liquid cold plates include aluminum, copper, and stainless steel, each offering unique thermal conductivity properties.
- Filler Metals: The selection of filler metals is crucial for ensuring a solid bond and optimal thermal transfer. Alloys commonly used for brazing include silver, copper, and nickel-based alloys.
Ensuring Thermal Efficiency
The brazing process plays a pivotal role in the thermal efficiency of the liquid cold plate. Properly brazed joints ensure minimal thermal resistance, facilitating efficient heat transfer from the component to the coolant.
Design Considerations for Custom Brazing Liquid Cold Plates
When customizing brazing liquid cold plates for specific applications, several key design factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance.
Critical Factors in Cold Plate Design
- Fluid Dynamics: Understanding the coolant flow within the cold plate is essential. The design should promote efficient fluid flow while minimizing pressure drops.
- Thermal Efficiency: The cold plate must be designed to maximize heat transfer. This includes considering the surface area in contact with the coolant and the thermal conductivity of the materials used.
- Component Layout: The placement of components on the cold plate should be optimized for uniform heat distribution, ensuring that all parts are adequately cooled.
Customization for Specific Applications
Custom brazing liquid cold plates can be tailored to meet the unique requirements of different applications. For instance, in high-power electronics, the cold plate may need to be designed to handle higher heat loads, while in aerospace applications, weight might be a more critical factor.
Collaboration with Manufacturers
Working closely with experienced brazing liquid cold plate manufacturers is crucial. They can provide valuable insights into the feasibility of different designs and help fine-tune the specifications to meet specific cooling needs.
Common Applications of Brazing Liquid Cold Plates
Because of their efficiency and customizability, brazing liquid cold plates find applications in various industries. Understanding these applications can provide insights into how these cooling solutions can be tailored for multiple needs.
Major Application Areas
- Electronic Cooling: Used extensively in the cooling of high-performance computers, servers, and power electronics, where efficient heat dissipation is critical.
- Medical Equipment: Essential in medical imaging and laser equipment, where precise temperature control is necessary for accurate results and equipment safety.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Utilized in solar panels and wind turbines to manage the heat generated, thus enhancing efficiency and longevity.
Case Studies
Using real-world examples of brazing liquid cold plates can illustrate their effectiveness. For instance, a case study on their use in high-speed computing can demonstrate how they manage the intense heat generated by processors, ensuring optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Manufacturer for Custom Solutions
Selecting the proper manufacturer is critical for custom brazing liquid cold plates. This choice can significantly impact the cooling solution’s quality, efficiency, and reliability.
Criteria for Selecting a Manufacturer
- Expertise and Experience: Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in producing high-quality brazing liquid cold plates. Their expertise can be valuable in designing and manufacturing efficient cooling solutions.
- Customization Capabilities: Ensure the manufacturer can customize cold dishes according to your requirements, including unique designs, materials, and performance specifications.
- Quality Assurance: Check for quality certifications and standards compliance, indicating a manufacturer’s commitment to producing reliable, high-standard products.
Collaborative Process
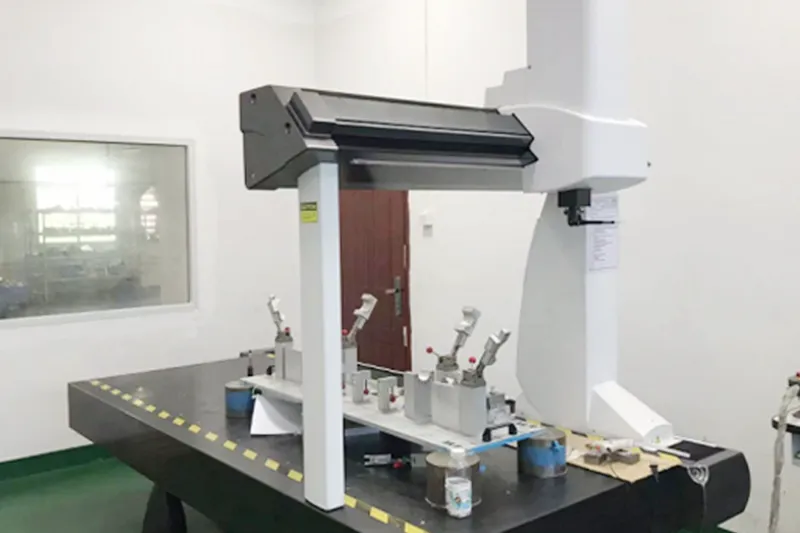

Working with a manufacturer should be a collaborative process. A good manufacturer will engage with you to understand your specific cooling needs, offer design recommendations, and provide prototypes for testing and validation.
Conclusion: Embracing Brazing Liquid Cold Plate Technology for Advanced Cooling
Brazing liquid cold plates represent a significant advancement in cooling technology, offering customizable, efficient, and reliable solutions for various applications. As the demand for more effective cooling systems grows, understanding and leveraging the capabilities of brazing liquid cold plates becomes increasingly essential. By collaborating with the right manufacturing partners, businesses and engineers can develop tailored solutions that meet their specific cooling challenges, driving innovation and efficiency in their fields.