Introduction
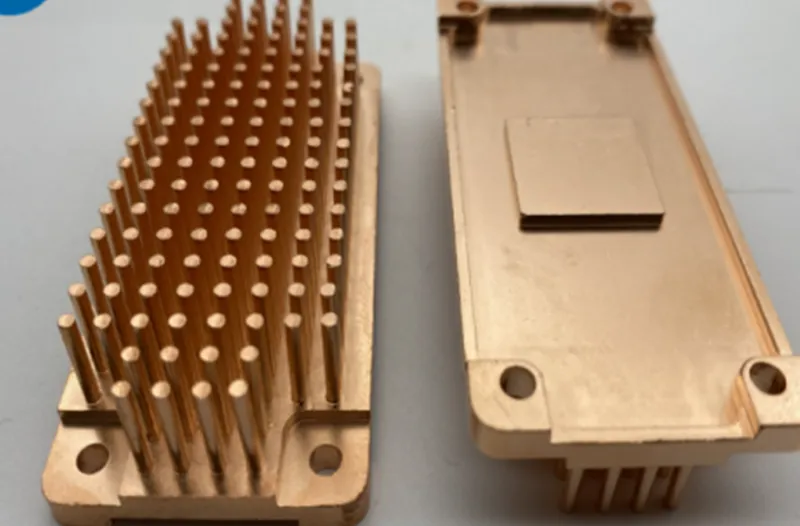

Heat sinks play a crucial role when managing heat in various electronic devices. They help dissipate heat generated by electronic components, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance. Heat sinks come in different types, each with unique advantages and disadvantages. In this blog post, we will focus on the benefits of cold forged heat sinks and discuss the circumstances in which they are preferred over other types, such as extruded or skived heat sinks. Whether you’re new to the concept of heat sinks or already familiar with the topic, this post aims to provide valuable insights into cold forged.
The Basics of Heat Sinks
Before diving into the specifics of cold forged heat sinks, let’s briefly touch upon the basics. Heat sinks are passive cooling devices made from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper. Their primary function is to absorb and dissipate heat from electronic components, ensuring their temperature remains within acceptable limits.
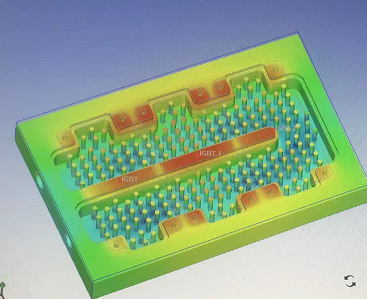
Heat sinks work through a mechanism called conduction. As electronic components generate heat, that heat is conducted away from the component’s surface and into the heat sink. From there, the heat is rapidly dissipated into the surrounding environment, allowing the part to remain at a safe operating temperature.
Understanding Cold Forged Heat Sinks
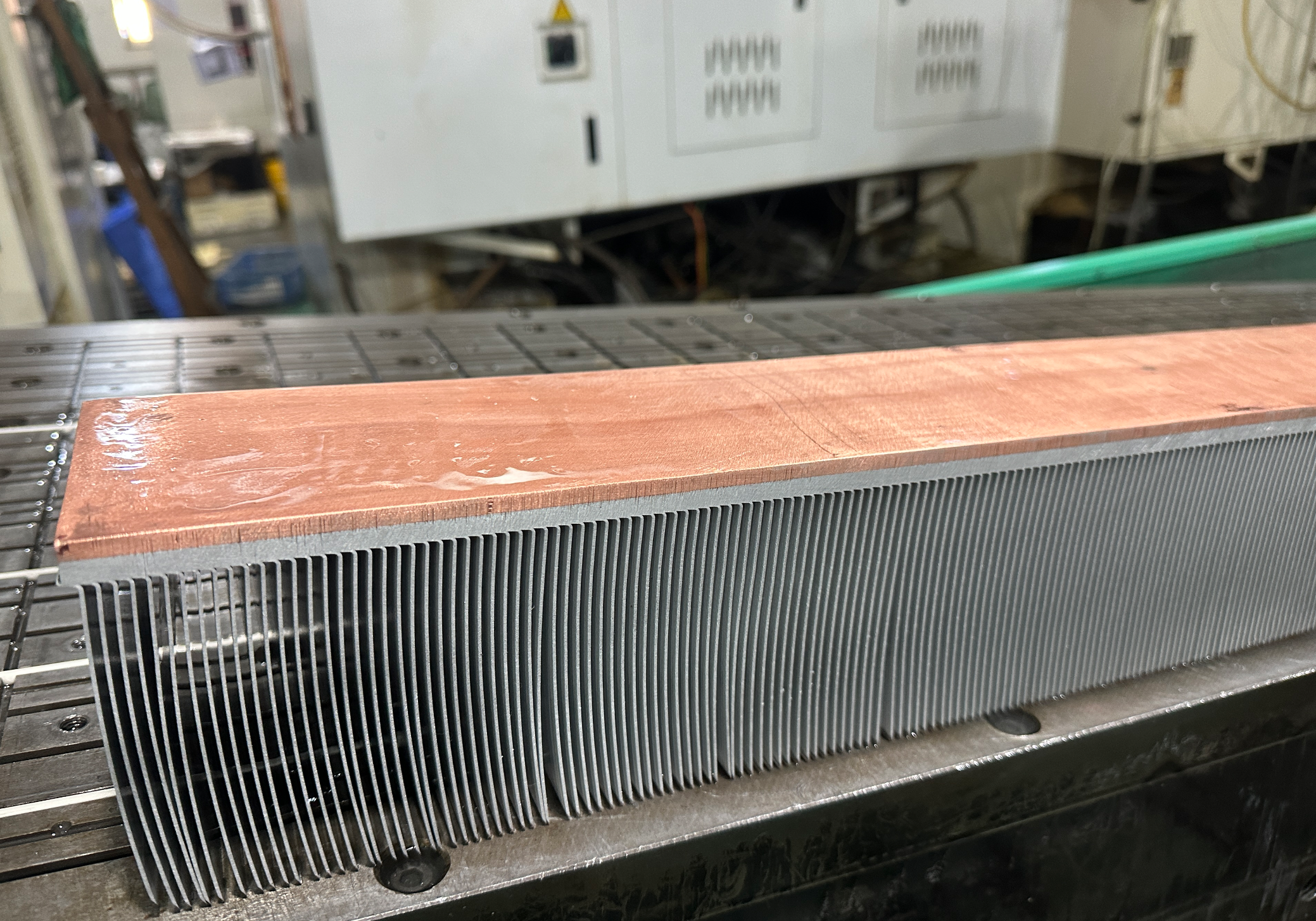
Cold forged heat sinks are a type of heat sink that offers several advantages compared to extruded or skived heat sinks. These heat sinks are manufactured using a specialized cold forging process, which involves shaping metal into complex heat sink geometries without extensive machining or tooling. Cold forging involves applying pressure to a metal billet at room temperature, resulting in a highly efficient heat sink with excellent thermal conductivity.
Advantages of Cold Forged
1. Enhanced Thermal Performance
One of the primary advantages of Radiators using the cold forging process is their superior thermal performance. Due to the forging process, Radiators using the cold forging process have a higher thermal conductivity than extruded or skived heat sinks. This means they can efficiently transfer heat away from electronic components and into the surrounding environment, reducing the risk of overheating.
The superior thermal performance of cold forged heat sinks is particularly advantageous in applications that require high power dissipation or operate under demanding conditions. For instance, in power electronics, where components generate significant heat, Radiators using the cold forging process can help maintain optimal operating temperatures, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the devices.
2. Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Another significant advantage of cold forged heat sinks is their lightweight nature. Cold forging allows for the creation of intricate heat sink designs with reduced material usage while maintaining the desired thermal performance. This lightweight characteristic is especially advantageous in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in the aerospace or automotive industries.
In addition to being lightweight, Radiators using the cold forging process are also cost-effective. The cold forging process allows for high-volume production with minimal material waste, making them a more economical choice than other heat sink manufacturing methods.
3. Customizable Designs
Cold forged heat sinks offer a high degree of design flexibility, allowing for creating custom shapes and geometries based on specific application requirements. The cold forging process enables the manufacturing of intricate fin patterns and other heat sink features that enhance thermal performance.
This design flexibility is precious when space constraints or unique component arrangements require a customized heat sink solution. Radiators using the cold forging process can be tailored to fit specific electronic assemblies, maximizing cooling efficiency and overall system performance.
4. Improved Mechanical Strength
Cold forged heat sinks possess superior mechanical strength compared to other heat sink types. The forging process aligns the metal grains, resulting in a denser and stronger material structure. This increased strength allows Radiators using the cold forging process to withstand higher shock, vibration, and mechanical stress levels.
The robust nature of Radiators using the cold forging process makes them well-suited for applications where mechanical stability is crucial, such as in industrial equipment, ruggedized electronics, or transportation systems.
When Are Cold Forged Heat Sinks Preferred?
Having understood the advantages of heat sinks in cold forged, let’s explore the circumstances in which they are preferred over other types of heat sinks:
1. High-Power Applications
Cold forged heat sinks are often preferred in applications where electronic components generate substantial heat, such as power electronics or high-power LED lighting. The superior thermal conductivity and efficient heat dissipation capabilities of Radiators using the cold forging process make them ideal for managing the elevated temperatures associated with high-power applications.
2. Weight-Constrained Environments
As mentioned earlier, cold forged heat sinks are lightweight due to their optimized design and reduced material usage. This characteristic makes them highly suitable for weight-constrained environments, such as aerospace and automotive applications. By opting for Radiators using the cold forging process, manufacturers can achieve the desired cooling performance while minimizing the overall weight of their electronic systems.
3. Compact Systems with Limited Space
Cold forged heat sinks prove advantageous in compact electronic systems where space is limited. The customizable design capabilities allow for creating of heat sinks that can fit snugly within tight spaces, ensuring efficient heat dissipation without compromising overall system dimensions. enable engineers to maximize cooling performance while maintaining a compact form factor.
4. Harsh Environmental Conditions
The robust mechanical strength of makes them highly suitable for applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions, such as outdoor installations or industrial settings. These heat sinks can withstand shocks, vibrations, and mechanical stresses, ensuring long-term stability and reliability of the electronic components they cool.
Conclusion
Cold forged heat sinks offer numerous advantages over other heat sinks, such as extruded or skived heat sinks. Their enhanced thermal performance, lightweight nature, customizable designs, and improved mechanical strength make them preferable in various circumstances.
Cold forged provide an excellent solution if you’re looking to manage heat in high-power applications, weight-constrained environments, compact systems, or harsh environmental conditions. By harnessing the benefits of cold forging technology, manufacturers can ensure optimal cooling and reliable performance for their electronic devices.
If you’re in the market for heat sinks, consider the specific requirements of your application and evaluate whether cold forged heat sinks align with your needs. Consulting with an experienced heat sink manufacturer can provide further guidance and expertise in selecting the most suitable heat sink solution for your project.
Remember, effective heat management is crucial for the longevity and performance of your electronic devices. By choosing the right heat sink, such as a cold forged heat sink, you can ensure the efficient dissipation of heat and protect your valuable components from damage caused by excessive temperatures.