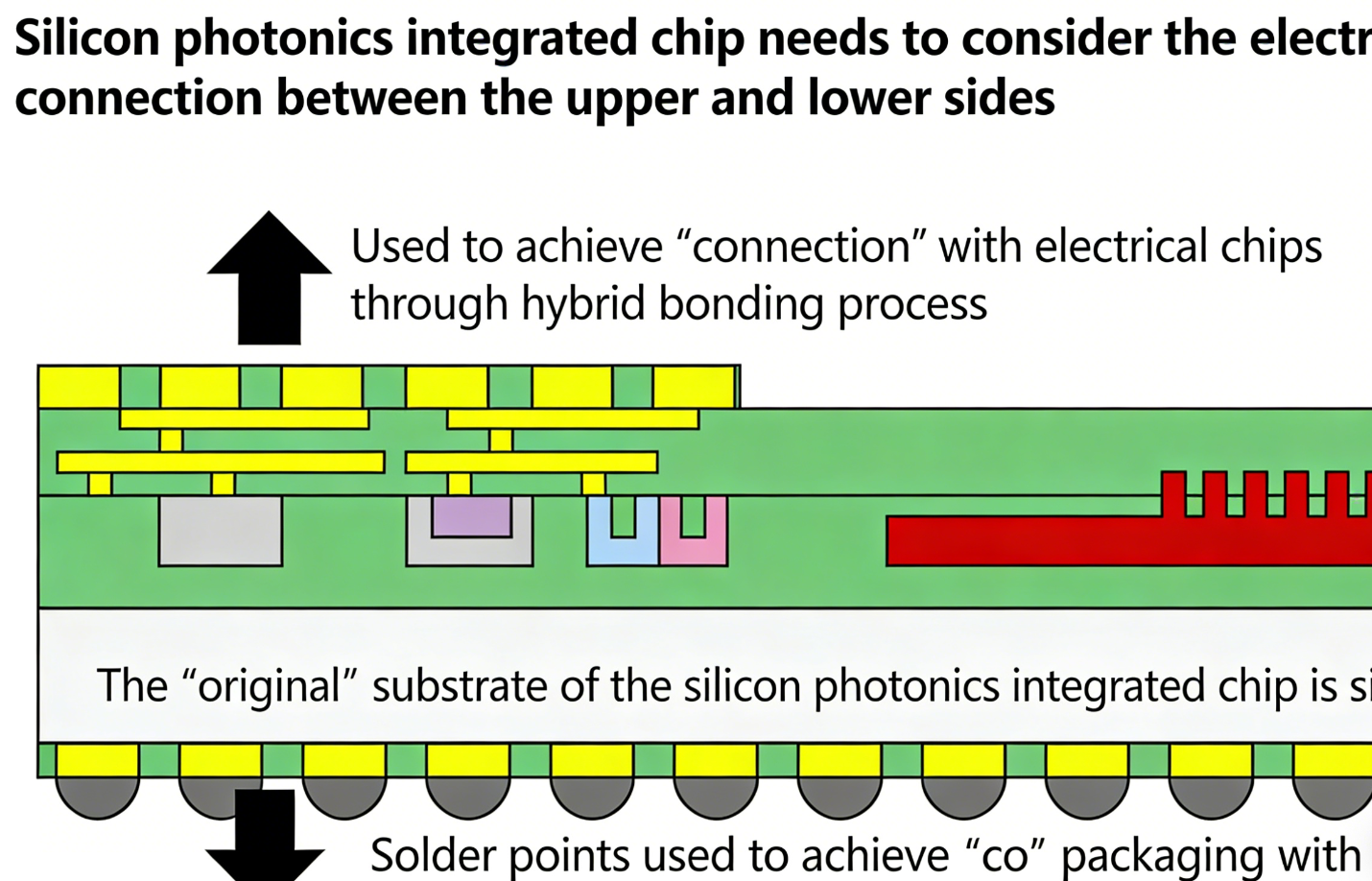
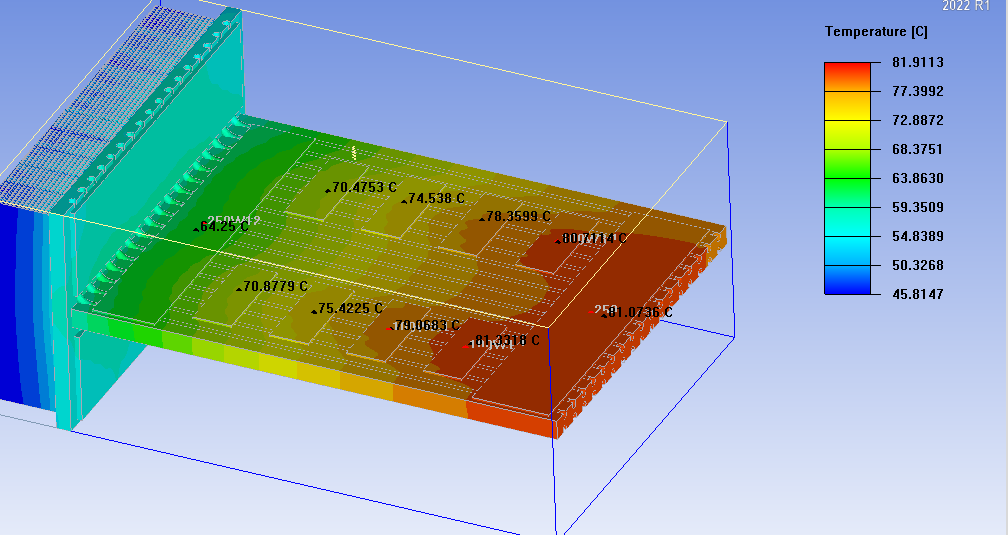
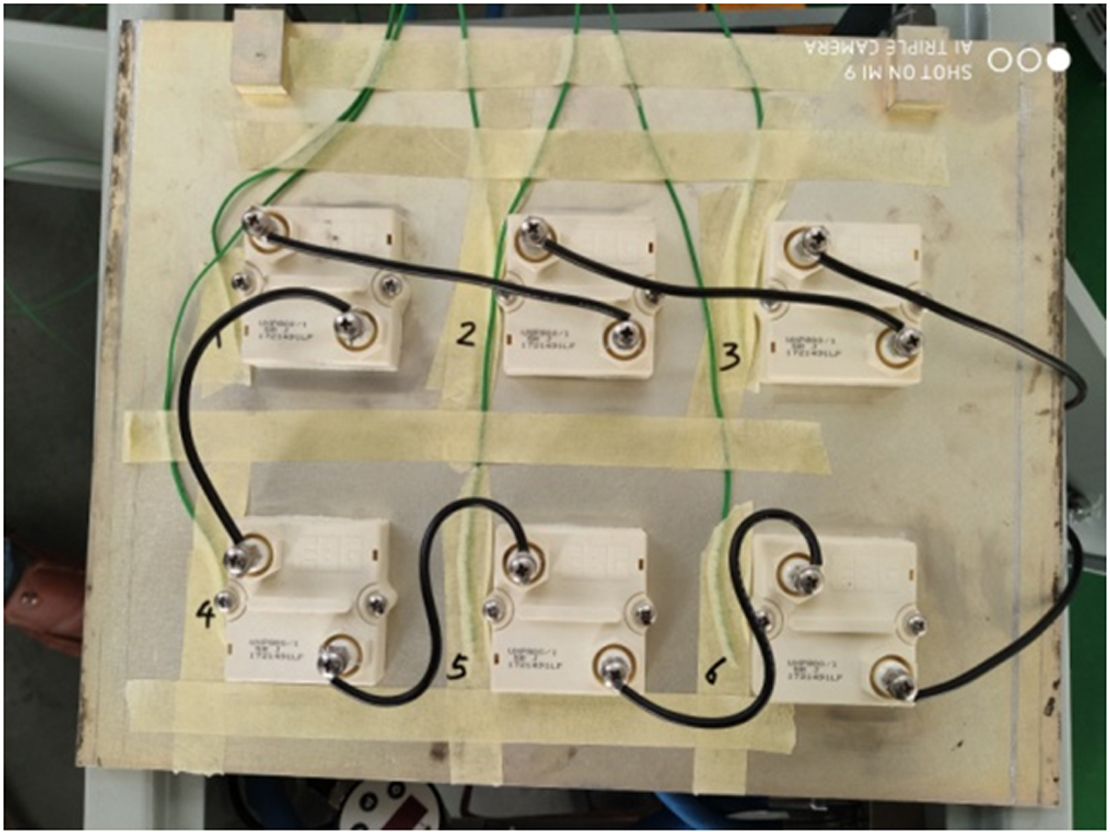
If you regularly use electronic machines, you may want to use some cooling devices because they produce a lot of heat.
This brings about the application of the heatsink into an electronic machine’s working state to cool.
Unlike in the early introduction, where it was only used for large computers because of the excessive heat they produce, it is now used in almost every electronic device as they must produce heat no matter how little and can relatively be harmful if not managed properly.
But many may want to ask what material is the best to produce heatsink? What material is the best for specific applications over another?
Truly selection of heatsink material can be a bit challenging. Why? Because even though the most used material for heat sinks is Aluminum, copper absorbs heat more.
So why is it predominantly in use? We have provided every detail about copper and Aluminum, their advantages, and which is best for your business in this article.

What Is Copper Heat Sinks?
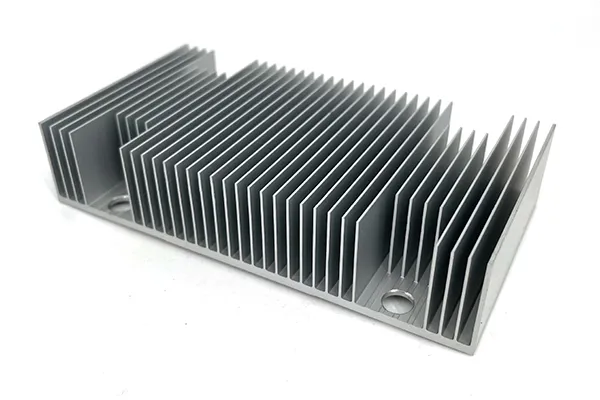
The equipment implemented in most electronic engines to drive away heat or absorb it is a Heat sink. Primarily found in CPUs, chips, computers, and also cell phones. They are essential to keep machines from overheating.
Without them, a whole electronic system is at risk of damage as the subsequent heat produced by it is dangerous.
However, a heat sink made of copper material is the copper heat sink.
Usually, copper, Aluminum, and silver are the most popular for making heat sinks.

What Is Aluminum Heat Sinks?
An aluminum heat sink is a heat sink made from aluminum. As mentioned above, aluminum is primarily used for heat sinks.
They can be seen as the most affordable heat sink.
How do they work?
The principle of a heat sink’s operation is that it is installed inside an electronic device and transfers the produced heat to a given fluid medium (coolant)/to move it away from the electronic and cool it.
The medium used to cool it can be liquid or air. The heat conducted by the heat sink cools off by the coolants(air or liquid). Hence the need for a relatively large surface area for the heat sink to absorb heat effectively and cool it. The heat sinks are made of metals.
Depending on the temperature operation of the electronics, a more effective heat sink will be implemented for effectiveness.
Also, the nature of the fin on the heat sink matters. The fin serves as the place where heat is transferred for cooling. Its thermal resistance makes it able to withstand conducting heat. However, if the fin is tightly packed and long, it might not conduct heat effectively.
In a nutshell, heat sinks work by:
● The heat produced by electronics conducts to its surface.
● The heat then travels to the heat sink, which is in contact with the electronics.
● Through conduction, the heat travels around the heat sink surface area till it gets to the coolants.
● The heat is then cooled. And the cycle continues.
Applications of the copper and aluminum heat sink
Whichever material(copper or aluminum) is used to make a heat sink, and it is applied in a wide range. Such as:
● Motor housing coolant
● Coolant for IT telecommunication
● Units for welding
● UPS(uninterruptible power supply)
● Traction drives
● Electric vehicle control cooling
● Cooling for battery pack solution
Manufacturing types
Just like material differences, the nature of the manufacturing of the heat sinks also makes them distinct. See the various manufacturing types below:
| ● Forging and die casting: This manufacturing method is best for heat sinks that are to be thick. They are perfect for voluminous production as they have low unit costs. They provide flexibility in design also. But the forged method creates issues with the design and management of airflow. |
| ● CNC Machining: Normally, CNC machining is a slow and costly manufacturing option. It can be helpful when a heat sink has an intricate design or high thermal conduction requirements. |
| ● Skirving fin: The heat sink produced by the skirved fin is cost-effective. Their fins tend to be thin. Applicable in high-strength operation. |
| ● Zipper fin: The heat sinks are produced with tightly packed fins. The heat sink has a low weight which is ten, to explain the manufacturing process’s low cost. |
| ● Stamping: Stamping heat sinks are used for low-power applications. They are cheap compared to other heat sinks. |
| ● Bonded fin: Heat sinks produced by this method usually contain different materials. It is recommended for heat sinks that will be big. |
Differences between both heat sinks
Copper vs. Aluminum Heatsink: heat dynamics
In times of heat dynamics, copper begets the upper hand. This is because it conducts heat better than aluminum. Also, copper has a very high melting point, and it is less reactive compared to aluminum.
All this indicates that copper heat sinks will spread heat better effectively, withstand high temperatures and take a longer time to corrode respectively.

Copper vs. Aluminum Heatsink: Thermal conductivity
The copper heat sink conducts heat faster than aluminum ones. Copper with around 400 m/k while aluminum with about 87m/k.

Copper vs. Aluminum Heatsink: Cooling
Just as copper heat sinks conduct heat more effectively, they also conduct the cooling effect more effectively and faster than aluminum.
Unlike aluminum heat sinks, copper ones do well without coatings; they are more dependable.

Copper vs. Aluminum Heatsink: Weight
In this case, aluminum heat sinks are employed when there is a need to make light heat sink equipment.
This is because copper is heavier than aluminum. When you need to compromise weight, aluminum is recommended.

Copper vs. Aluminum Heatsink: Costs
This is one of the principal reasons why aluminum heat sinks are more in use. In fact, aluminum costs more than half less than copper. And so, making an aluminum heat sink is cheaper than making a copper one. The process is easy to carry out, and no high-category metal is needed.
Aluminum is also lighter than copper, making it easier to transport.
Unlike copper, heat sinks where copper material is relatively expensive, so a complex manufacturing method is used to work on it.

Copper vs. Aluminum Heatsink: Availability
Aluminum is the fast go-to option for heat sinks as it is the most popular. In addition to that, they are a wide range of colors, design, and cost option to pick from. Unlike copper, you can get the exact specification if you want something specific.

Which Heatsink Is Right For You?
To decide which heat sink is best for your service, you must consider all its aspects and your business needs.
For instance, aluminum is the most popular for heat sinks, but that does not mean copper is less effective for heat sinks or that aluminum should be your preferred choice.
Aluminum might be cheap, but copper is recommended for high heat conductivity applications.
Also, copper heat sinks are allowed to be complex and intricate, unlike aluminum.
Though complex geometrical copper heat sinks can be produced by CNC Machining and die casting, extruded aluminum heat sinks can also serve your needs.
It is important to note also that it is expected that you might be looking for a lighter heat sink for your electronics as the world keeps advancing and devices want to improve usefulness as well as be as light as possible. Then do not just go for aluminum and neglect the benefits copper can bring to your service as you can compact the two materials into a heat sink.
For instance, your heat sink will be based on aluminum to make it light and the copper plate for a high conduction rate.
A drawback to this method is that sometimes the aluminum does not pact well with the copper, and the copper plate will be dangerous. This problem is mainly found in less expensive heat sinks.
Cheap options cost more relatively
One important thing also to note is that a heat sink produced in a cheap standard with whatever material tends to cost more relatively in the long run.
This is because the cheaply produced heat sinks contain fans that use sleeve bearings in contrast to the ball bearing of the more expensive ones. The sleeve bearings usually develop issues with lubrication over time and spoil, unlike the ball bearings, which cost more to make but last longer.
Make sure to compare all these factors to your initial investment and business purpose; by doing so, you can easily pick the best option.
Conclusion
If you need the same suggestion on the heat sink to use for your specific business necessities, our engineers at Kenfatech are specially trained for thermal services and will give the best complete services you require.
We have a base of more than 300 engineers that have more than two decades of experience in serving top businesses around the world.
Our technician’s services are sure not to compromise your production quality while providing quick services.
Get the best heat sink material for your business within the shortest time frame by contacting us now.