
The importance of thermal management in charging stations cannot be overstated, as it ensures the proper operation and longevity of the charging equipment. Here are several key reasons explaining why thermal management is crucial for charging stations:
1. Ensuring charging efficiency: Charging stations generate heat during operation, and if this heat is not effectively dissipated, the charging equipment may overheat, resulting in reduced efficiency. Effective thermal management maintains the working temperature of the charging equipment within an acceptable range, ensuring maximum charging efficiency.
2. Extending equipment lifespan: High temperatures have adverse effects on the lifespan of electronic devices. Components such as electronic elements, batteries, and circuit boards in charging stations may become damaged or prematurely aged under excessive heat. Proper thermal management measures reduce the working temperature of charging stations, prolonging the equipment’s lifespan and reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
3. Improving safety: Elevated temperatures can lead to equipment malfunctions, short circuits, or other safety issues in charging stations. Thermal management measures help control the temperature of the charging equipment, reducing the risks of fire hazards, electric shocks, and enhancing safety during operation.
4. Enhancing user experience: In high-temperature conditions, charging equipment performance may be limited, and charging speeds may decrease. Effective thermal management ensures stable operation, consistent charging speeds, and a reliable user experience.
How to manage the heat of charging pile equipment?
Effective thermal management of charging stations is crucial for ensuring their proper operation and extending the lifespan of the equipment. The following are some common methods employed for thermal management of charging stations:
1. Heat dissipation design: A well-designed heat dissipation system is the core of thermal management. Ensure that the charging station is equipped with adequate heat sinks or cooling fans and install them in appropriate locations to facilitate heat conduction and dissipation.
2. Use of high thermal conductivity materials: Utilizing materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum, on critical components of the charging station improves heat transfer efficiency, enabling quick transfer of heat to heat sinks or cooling fans.
3. Maintaining airflow: Ensure that air can freely circulate around the charging station to facilitate effective heat dissipation. Avoid obstructing airflow around the charging station by keeping objects away from it.
4. Temperature monitoring and protection: Install temperature sensors to monitor the operating temperature of the charging station. When the temperature exceeds the safe range, implement measures such as automatically reducing charging power or stopping the charging process to protect the equipment.
5. Control environmental temperature: Minimize exposing the charging station to high temperatures or direct sunlight. If the charging station is installed outdoors, consider providing shading measures or using sunshades to mitigate the impact of environmental temperature on the equipment.
6. Optimize system design: Optimize circuit design and power management strategies of the charging station to reduce heat generation and loss, thereby lowering the working temperature of the equipment.
7. Regular maintenance and cleaning: Regularly clean the charging station and its heat dissipation components to ensure a dust-free and unobstructed airflow, thereby maintaining optimal heat dissipation effectiveness.
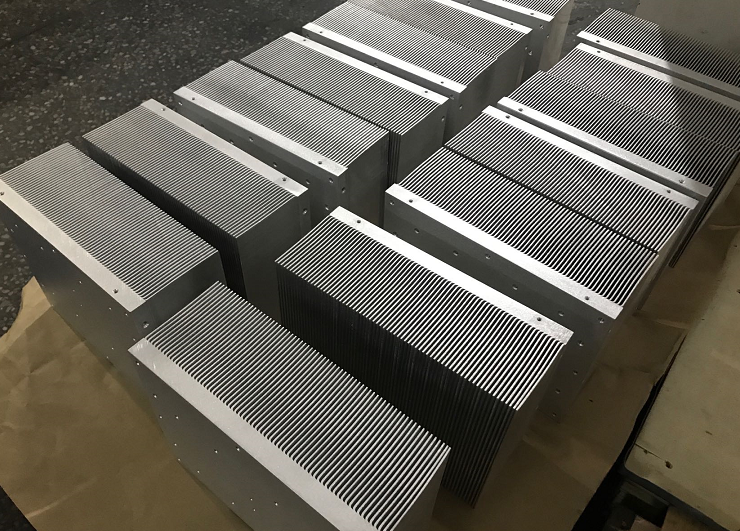
The commonly used heat dissipation techniques for thermal management of charging stations include the following:
1. Cooling fans: Cooling fans are a common heat management component. They accelerate airflow to aid in heat dissipation. Cooling fans can be DC or AC fans, and the appropriate fan model and installation method are chosen based on the design and requirements of the charging station.
2. Skived fin heat sinks: Heat sinks or skived fin heat sinks are heat dissipation components that enhance heat dissipation by increasing the surface area. They are typically made of metal materials such as aluminum or copper, which have good thermal conductivity. By enlarging the contact area, heat sinks facilitate heat conduction and dissipation.
3. Heat pipes: Heat pipes are heat dissipation components that transfer heat from one area to another through a conduit filled with a thermal medium such as thermal paste or liquid. Heat pipes, usually made of copper or aluminum, effectively transfer and disperse heat from critical components of the charging station to the heat sink.
4. Vapor chambers: Vapor chambers are highly efficient heat management technology that utilizes a vacuum-sealed chamber and a working fluid to achieve heat conduction and balance. Made of copper or aluminum, vapor chambers efficiently transfer and distribute heat in charging stations.
5. Liquid cooling systems: Liquid cooling systems use liquid as a medium for heat transfer, circulating it within the charging station to absorb and dissipate heat. These systems typically include components such as coolers, pumps, and pipelines, providing robust heat dissipation capabilities for high-power-density charging equipment.
The choice of heat dissipation technique depends on factors such as the design requirements, power density, available space, and budget of the charging station. For most charging station applications, cooling fans, heat sinks, and heat pipes are the most common and cost-effective choices. Liquid cooling systems and vapor chambers are suitable for high-power-density charging stations operating under extreme conditions.



