This paper mainly introduces the basic knowledge of thermal design of electronic equipment, and thermal designers should be familiar with these basic knowledge if they want to conduct thermal analysis or become a qualified designer of electronic heat dissipation. Only the designer master the basic knowledge of heat conduction, according to the working mode of equipment and the amount of heat generation, can design one or several suitable for industrial site heat conduction cooling mode, to meet the needs of industrial site equipment heat conduction.
Key words
Heat transfer mode
mass conservation equation
Design method and procedure of heat dissipation of heating device
Natural cooling
Forced ventilation cooling
Direct liquid cooling
Indirect liquid cooling plate
Article contents
The second law of thermodynamics states that heat is always spontaneous and irreversible, from high temperature to low temperature, that is, as long as there is a temperature difference, heat will spontaneously transfer from high temperature to low temperature, forming heat exchange. There are three modes of heat transfer: conduction, convection and radiation. They may appear alone, or in two or three forms at the same time.
The conservation of mass in fluid motion means that the total mass of fluid flows through a certain space remains constant, and any flow problem must satisfy the law of conservation of mass. The continuity equation of the control body is:

The law of conservation of momentum is one of the most important and universal conservation laws in nature. It applies to both macroscopic objects and microscopic particles. It is suitable for both low speed moving objects and high speed moving objects. It applies to both conservative and non-conservative systems. The law of conservation of momentum is a fundamental law that any moving system, including any flowing system, must obey when it is not subjected to external forces. This equation can be interpreted as: the resultant force acting on a fluid in a control body is equal to the cumulative amount of momentum exiting the control body per unit time minus momentum entering the control body per unit time plus momentum of the fluid in the control body per unit time. The momentum equation for the control body is:

The design of heat dissipation and conduction is an important aspect of equipment reliability design. Electronic equipment as long as the electricity has heat, is the heat source, the heat generated is equal to the dissipation of power. Dissipated power (heating power) is the basis of thermal design and can be determined by experimental and theoretical calculations. Generally, increase the safety factor, conservative value, appropriate higher. Thermal design is generally designed under the most severe conditions: the highest ambient temperature and the maximum heat dissipation. In general, the design of heat dissipation and conduction of electronic equipment should comply with the following aspects and steps:
(1)Determine the heat dissipation area of the heating device, the ambient temperature limit range of the radiator or the surrounding air medium;
(2) Determine the convective density and dissipation mode of heat;
(3) Carry out stress analysis on a few key heating components, determine their maximum allowable temperature and power consumption, and analyze their failure rate under the temperature relationship;
(4) Calculate the thermal density according to the installation method of the heating device and the whole equipment;
(5) The maximum working temperature of the surface is determined by the internal thermal resistance of the device;
(6) Calculate the total thermal barrier value between the device and the final heat dissipation surface;
(7) Calculate and distribute the thermal barrier according to the heat generation measurement and other factors, and evaluate it to determine the heat conduction mode and cooling mode
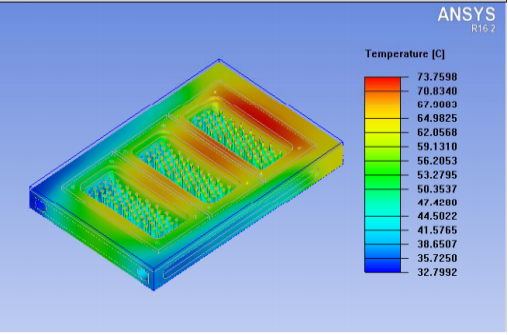
Placed natural cooling is the single action of heat dissipation, convection and radiation heat transfer or a combination of more than two forms of heat transfer, the advantages of high reliability, low cost. Natural cooling is greatly affected by the external environment, and there are easy obstacles to heat conduction in the conduction path, increasing the heat conduction resistance, thus reducing the conduction speed of air heat transfer and the flow dose of air. Therefore, in the case of interference from the environment outside the equipment, this cooling method is a relatively simple, efficient, cost-effective cooling method. It does not require coolant transfer equipment such as fans or transfer pumps, and avoids system reliability problems caused by wear or failure of equipment components. Therefore, natural cooling methods should be preferred.
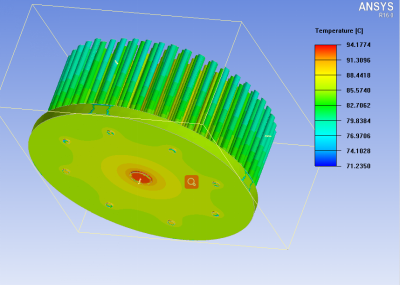
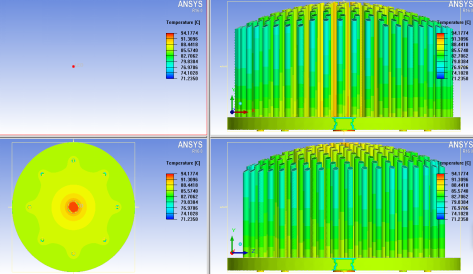
In the forced air cooling, high-power intensive integrated electronic equipment and more heat can not rely on the natural wind cooling equipment is more used, because it has a higher convective speed and greater flow than the air in the natural cooling, and several other heat conduction mode of forced cooling mode compared, this cooling mode has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, easy maintenance.
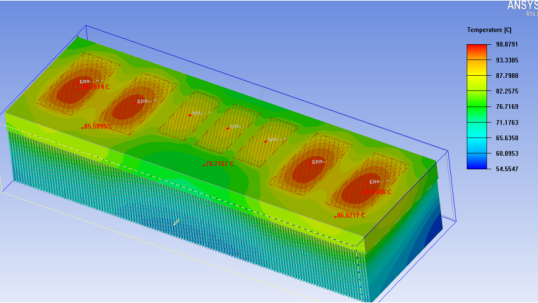
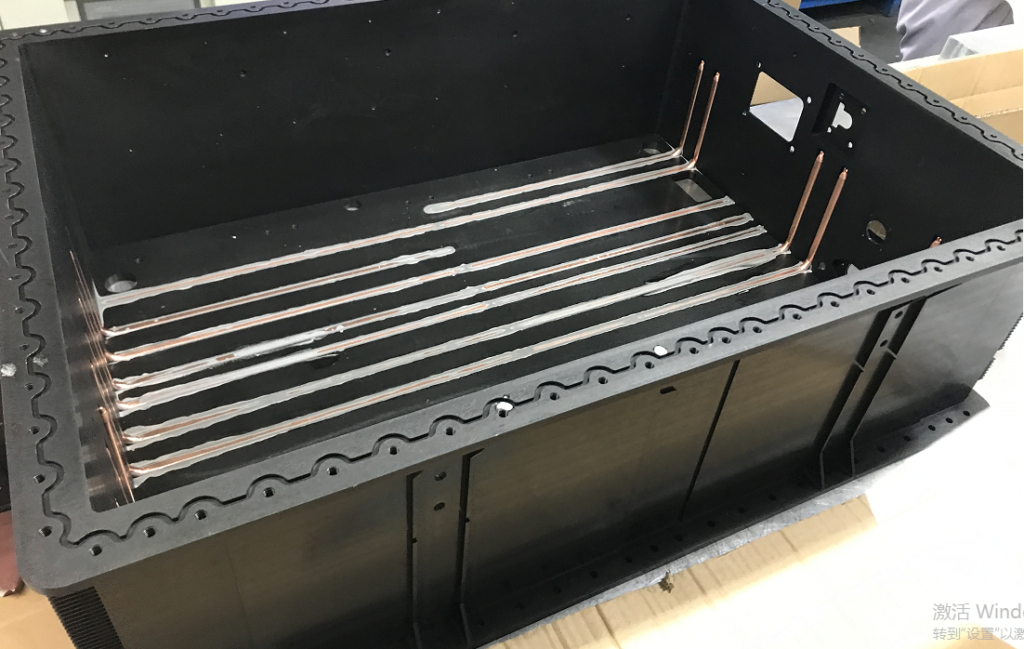
What we call direct liquid cooling is that the heating part of the electronic components of the equipment is directly in contact with the coolant for heat exchange. The heating components transfer the heat generated to the coolant, so that the heat reduces and the temperature of the coolant increases, and then the excess heat is lost by the coolant. This cooling method is suitable for equipment with high thermal density or high integration density of electronic components. The cooling method needs high characteristics of heating components and coolant. The coolant must meet the requirements of high boiling point, non-decomposition, non-volatilization and other characteristics at the working temperature of electronic equipment, and it must also meet the requirement that the coolant does not affect the function of the equipment.
Indirect liquid cooling , commonly known as indirect liquid cooling, refers to the coolant does not directly contact with the heating electronic components, but through the external equipment base plate and other intermediate modules of the heating components to contact the heat generation heat to the indirect coolant, cooling liquid after heating up and then through the surface of the coolant loss to achieve the purpose of indirect cooling. The design of indirect liquid cooling system mainly requires a good thermal conduction path between the heating source and the intermediate medium to reduce the thermal contact resistance as much as possible. In this method, the coolant does not contact with electronic components directly, which can reduce the pollution of electronic equipment, and the requirement of coolant is higher than that of direct cooling liquid, and the maintenance is simple.