At present, liquid cooling solutions for high-density servers in data centers are mainly divided into two categories: indirect liquid cooling technology and direct liquid cooling technology. This classification is based primarily on the indoor end form of liquid cooling solutions.
Key words
Indirect liquid cooling technology
Direct liquid cooling technology
Article contents
Indirect liquid cooling technology refers to the heat transfer process without direct contact between the server heat source and liquid refrigerant, mainly classified into the cooling plate and heat pipe. Among them, the cold plate is divided into “single-phase cold plate” and “phase change cold plate” according to whether phase change occurs in the heat transfer process of the refrigerant.
The heat pipe is divided into “two-stage heat pipe type” and “heat pipe + water cooling type” according to the heat dissipation form of the condensing end. At present, the most popular solution is single–phase cooling plate liquid cooling.
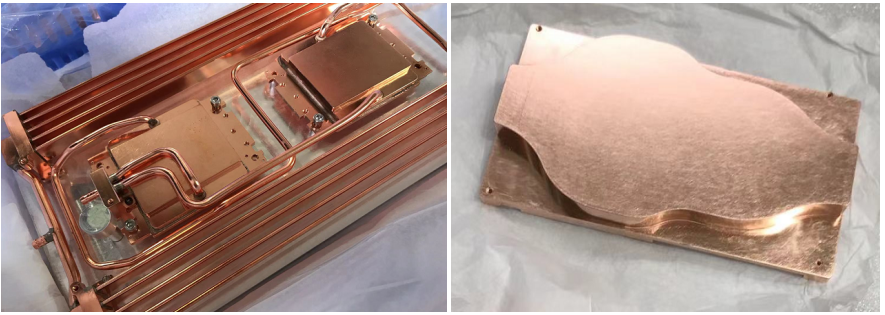
Huawei Fusion server liquid-cooled Server uses the single-phase liquid-cooled plate solution for cooling. The power density of a single cabinet can reach 45kW/rack. The sub-cooling agent uses deionized water +BTA corrosion inhibition agent, and the maximum influent temperature supported can reach 45℃, reaching the W4 liquid cooling level of DLC standard.
Taking the climate of Beijing as an example (the maximum annual extreme wet bulb temperature is 31.5℃), the cooling tower can be used to realize natural cooling throughout the year, and the PUE of the machine room can be reduced to 1.1 theoretically. In addition, the MTBF of the refrigeration system is improved because of the simplification of the refrigeration system.
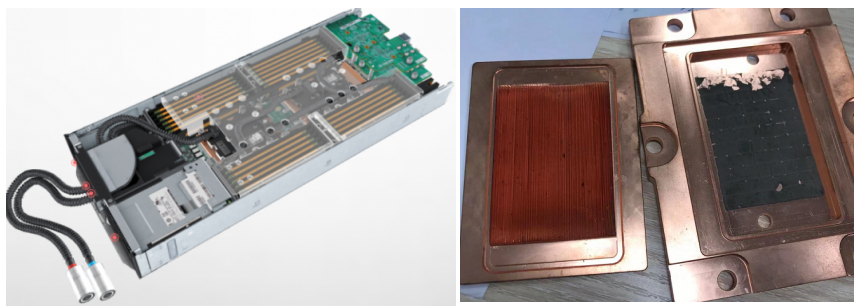
The structure design of the liquid cooling plate has a high coupling relationship with the server, and the universality is low, so the production cost is increased. Although the water-cooled head on the processor has been added with microchannel, injection, and other composite-enhanced heat transfer technology, the heat transfer capacity per unit area has been further improved, which needs to be improved.
At present, the Lenovo liquid cooling plate can support 270W power CPU; the Liquid cooling plate has high requirements on circulating cooling medium, such as PH, cleanliness, Ca+, and Mg+ ion concentration requirements of the cooling medium. These parameters will affect the heat transfer capacity, corrosion, circulating resistance, etc. The local resistance of the quick plug joint is significant, so it needs to be further optimized.
Direct liquid cooling technology refers to the heat transfer process of direct contact between coolant and electronic components, mainly classified into spray type, spray type, and immersion type. Spray type refers to the cooling liquid pressurized in the spray nozzle after atomization into tiny particle-size droplets, sprayed to the surface of electronic components, boiling heat transfer, and the heat away.
The spray type uses the characteristics of high-speed forced convection heat transfer to strengthen the heat transfer density, and the principle is similar to the spray type.
Immersion refers to the immersion of electronic components in the cooling liquid heat transfer, according to the heat transfer process, whether phase transition is divided into single-phase immersion and phase transition immersion. Submerged liquid cooling is currently in the market for small–scale commercial applications.
Ali’s Feitian · Kirin liquid cooling server generation products have been out of the laboratory, in the data room located in Zhangbei, to make the small-scale applications. The liquid cooling solution aims to achieve a single cabinet power density of 100kW/rack and uses 3M’s FC-72 fluorinated liquid with a boiling temperature of 56℃, which belongs to the category of phase change immersion cooling.
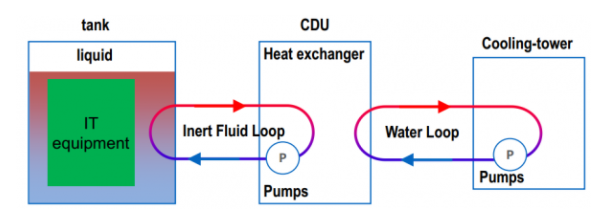
The coolant coil inside the Tank is heated and boiled with electronic components, and the gaseous fluorinated liquid condenses into liquid on the wall surface of the coolant coil to realize the transfer of heat from the electronic element to the coolant.
After the coolant is exchanged with the circulating cooling water inside the CDU through the plate heat exchanger, the heat is finally dispersed to the environment through the outdoor cooling tower.
At present, the inlet temperature of the coolant is 30℃, and the inlet temperature can be further increased in the subsequent optimization of the product to achieve the purpose of natural cooling throughout the year.
As for the current application case of submerged liquid cooling
technology, there are still several problems as follows:
The air-tightness design of the container. Because the heat transfer intensity of the fluorinated liquid in the container and the electronic element depends on the load rate of the electronic components, when the load rate fluctuation is relatively large, the change of the fluoride liquid vaporized per unit of time becomes more extensive, which leads to the pressure fluctuation in the container; Escape of fluorinated solution during maintenance.
Because of the phase change immersion heat transfer, when IT is necessary to replace or maintain one of the IT equipment in the container, a large amount of fluorinated liquid will escape in the process of plugging and removing IT equipment because another equipment business is still running.
As far as FC-72 is concerned, the fluorinated liquid belongs to greenhouse gases and has a stable structure, which means that the escaped fluorinated liquid will exist in the atmosphere for a long time and is difficult to decompose.
The cost of the electronic fluorinated solution is high. There are few manufacturers mainly concentrated in 3M Company, Shell, and other multinational enterprises, so it isn’t easy to reduce the cost in the short term.